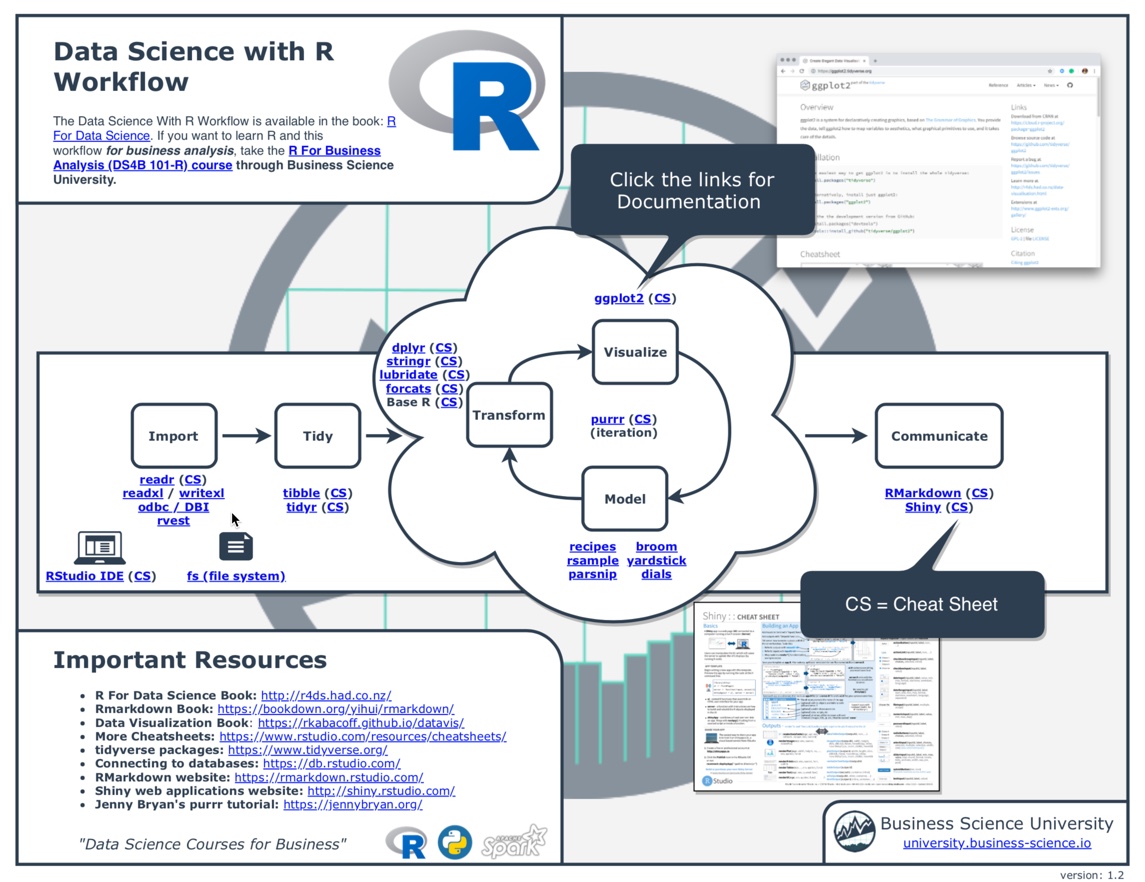
Filter Cheat Sheet R . The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. To the column values to determine which. use a filtering join to filter one table against the rows of another. keep rows that match a condition. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. what is dplyr. filter() picks cases based on their values. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. you can use the filter() function to filter a data frame based on certain criteria and the group_by() function to group a data frame by one or more.
from www.business-science.io
keep rows that match a condition. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. what is dplyr. you can use the filter() function to filter a data frame based on certain criteria and the group_by() function to group a data frame by one or more. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. use a filtering join to filter one table against the rows of another. filter() picks cases based on their values. dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria.
Ultimate Data Science with R Cheat Sheet
Filter Cheat Sheet R The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows. The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. To the column values to determine which. dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. you can use the filter() function to filter a data frame based on certain criteria and the group_by() function to group a data frame by one or more. what is dplyr. keep rows that match a condition. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. filter() picks cases based on their values. use a filtering join to filter one table against the rows of another. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in.
From www.reddit.com
LDAP Filters Cheat Sheet by pamymaf (2 pages) software nope filters ldap activedirectory Filter Cheat Sheet R The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows. keep rows that match a condition. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From permatron.com
Permatron Costeffective OEM Filter Cheat Sheet Filter Cheat Sheet R Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. To the column values to determine which. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. The filter() function is used to subset a data. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.rforecology.com
The essential functions of R cheatsheet R (for ecology) Filter Cheat Sheet R Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. To the column values to determine which. filter() picks cases based on their values. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. . Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From rstudio-conf-2020.github.io
Chapter 8 Filters and joins R for Excel Users Filter Cheat Sheet R Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. keep rows that match a condition. you can use the filter() function to filter a data frame based on certain criteria and the group_by() function to group a data frame by one or more. The filter() function is used to subset a data. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From cheatography.com
R BASIC Cheat Sheet by user111 Download free from Cheatography Cheat Filter Cheat Sheet R dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. keep rows that match a condition. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. use a filtering join to filter one table against the rows of another. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. filter() picks. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.datacamp.com
Data Manipulation with dplyr in R Cheat Sheet DataCamp Filter Cheat Sheet R Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. what is dplyr. use a filtering join to filter one table against the. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From mavink.com
R Shortcuts Cheat Sheet Filter Cheat Sheet R Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. use a filtering join to filter one table against the rows of another. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. keep rows that match a condition. you can use. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From studylib.net
Passive Filter Cheat Sheet Filter Cheat Sheet R the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. filter() picks cases based on their values. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. what is dplyr. The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows.. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.reddit.com
LDAP Filters Cheat Sheet by pamymaf (2 pages) software nope filters ldap activedirectory Filter Cheat Sheet R filter() picks cases based on their values. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. keep rows that match a condition. Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. what is dplyr. . Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION 05 1 wireshark display filter cheat sheet Studypool Filter Cheat Sheet R dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. what is dplyr. Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. To the column values to determine. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.datacamp.com
R Basics Cheat Sheet DataCamp Filter Cheat Sheet R keep rows that match a condition. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. filter() picks cases based on their values. use a filtering join to filter. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.pinterest.com
The Filter Cheat Sheet The Filtered Files Filters Fast Your 1 Resource for Air and Water Filter Cheat Sheet R Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows. Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. filter() picks cases based on their values. in this cheat sheet,. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.pinterest.de
R Programming Cheat Sheets Data science, Data science learning, Data visualization tools Filter Cheat Sheet R keep rows that match a condition. To the column values to determine which. you can use the filter() function to filter a data frame based on certain criteria and the group_by() function to group a data frame by one or more. The filter() function is used to subset a data frame, retaining all rows. Summarise() reduces multiple values. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From rforpoliticalscience.com
Cheat Sheets in R R Functions and Packages for Political Science Analysis Filter Cheat Sheet R dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical analysis, enabling researchers and. what is dplyr. To the column values to determine which. in this cheat sheet, you'll find a handy list of functions covering dplyr functions —all collected from our data. The filter() function is used to subset a. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From getcheatsheet.blogspot.com
R Data Table Cheat Sheet Cheat Sheet Filter Cheat Sheet R Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. filter() picks cases based on their values. keep rows that match a condition. dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. what is dplyr. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. Data manipulation is crucial to statistical. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From getcheatsheet.blogspot.com
R Data Table Cheat Sheet Cheat Sheet Filter Cheat Sheet R Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. the filter() function is used to subset the rows of.data, applying the expressions in. Summarise() reduces multiple values down to a single summary. To the column values to determine which. what is dplyr. you can use the filter() function to filter a. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION 05 1 wireshark display filter cheat sheet Studypool Filter Cheat Sheet R you can use the filter() function to filter a data frame based on certain criteria and the group_by() function to group a data frame by one or more. keep rows that match a condition. dplyr::filter(iris, sepal.length > 7) extract rows that meet logical criteria. filter() picks cases based on their values. To the column values to. Filter Cheat Sheet R.
From www.scribd.com
Low Cut Filter Cheat Sheet PDF Filter Cheat Sheet R Semi_join(x, y, by = null,.) return rows of x that have a match in y. use a filtering join to filter one table against the rows of another. what is dplyr. you can use the filter() function to filter a data frame based on certain criteria and the group_by() function to group a data frame by one. Filter Cheat Sheet R.